MyGet and GitHub Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication, or 2FA, is a way of logging into websites that requires more than just a password. GitHub has support for enabling 2FA to log in to their website and make use of hosted git repositories.
Since MyGet integrates with GitHub in several ways, let's explore some scenarios when GitHub 2FA is enabled.
Using the GitHub identity provider with MyGet
If you are logging in to MyGet using the GitHub identity provider, nothing changes. What does change is how GitHub handles the login: you will have to provide regular credentials as well as an additional token (obtained using an app or text message). The login will then be handled and once succesful, GitHub redirects back to MyGet.
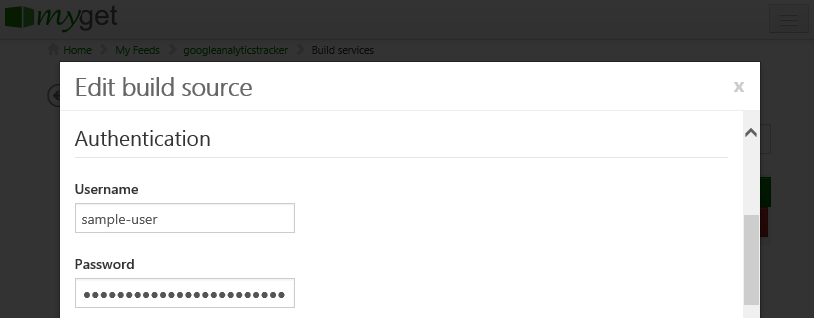
Using Build Services with Two-Factor authentication
When Two-Factor authentication is enabled on GitHub, consuming git from the commandline will require this personal access token to be entered. Since MyGet uses commandline git under the hood when running builds, this token will have to be entered through the MyGet web interface.
Note: You can create a personal access token for accessing GitHub by going to the application settings page. Use the generated personal access token for configuring the MyGet build.
Once you have created a personal access token, navigate to the Build Services tab for your MyGet feed and edit the build configuration(s) that requires GitHub 2FA authentication. In the username field, enter your GitHub username. In the password field, enter the personal access token generated through the GitHub website. After saving these settings, MyGet will be able to succesfully authenticate against GitHub again.
Read our contribution guidance or edit this page's source on GitHub.