Setting up your own Python registry has never been easier. MyGet allows you to create your own public or private Python registries in just a few clicks and work with your own Python packages. This section will guide you through it.
Creating a new feed
Browse to MyGet.org and log in using your preferred identity provider.
Complete your new MyGet profile by providing a username and password. These are your MyGet credentials, which you'll need to authenticate against private feeds on MyGet.org. From now on, you can also use these to log in on the MyGet.org web site.
Create a new feed that will serve as a registry and select the desired security template: public, private or community
- public: everyone has read access, only feed owners/managers can write
- private: only users with explicitly granted permissions can read or write (depending on permissions)
- community: everyone can read all packages + anyone can manage the packages they pushed to the feed
(optional) Invite collaborators through the feed security settings.
Next steps
Add packages to the feed by either uploading them through the web site, referencing/mirroring them from pypi.org
On each feed, packages can be added through the web UI.
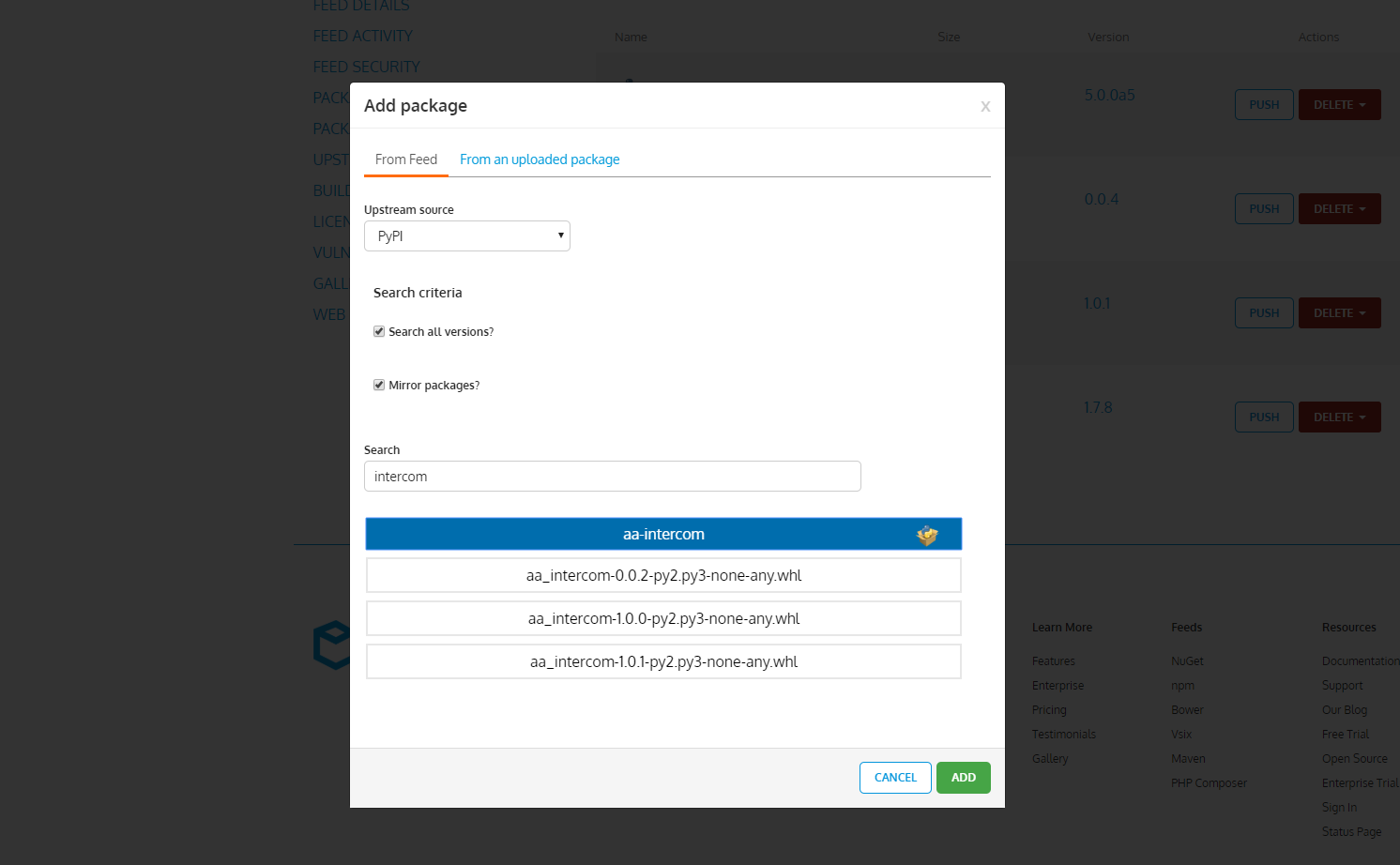
Keep in mind that currently MyGet does not support hosting tar.gz packages. Hovewer package which as a dependency has some other package which is available only in tar.gz can still be installed with „pip” tool.
If you type something in search field, the search is performed on pypi.org and returns all packages which names matches your term. Click on specific name and all .whl packages will be presented to you if they are available.
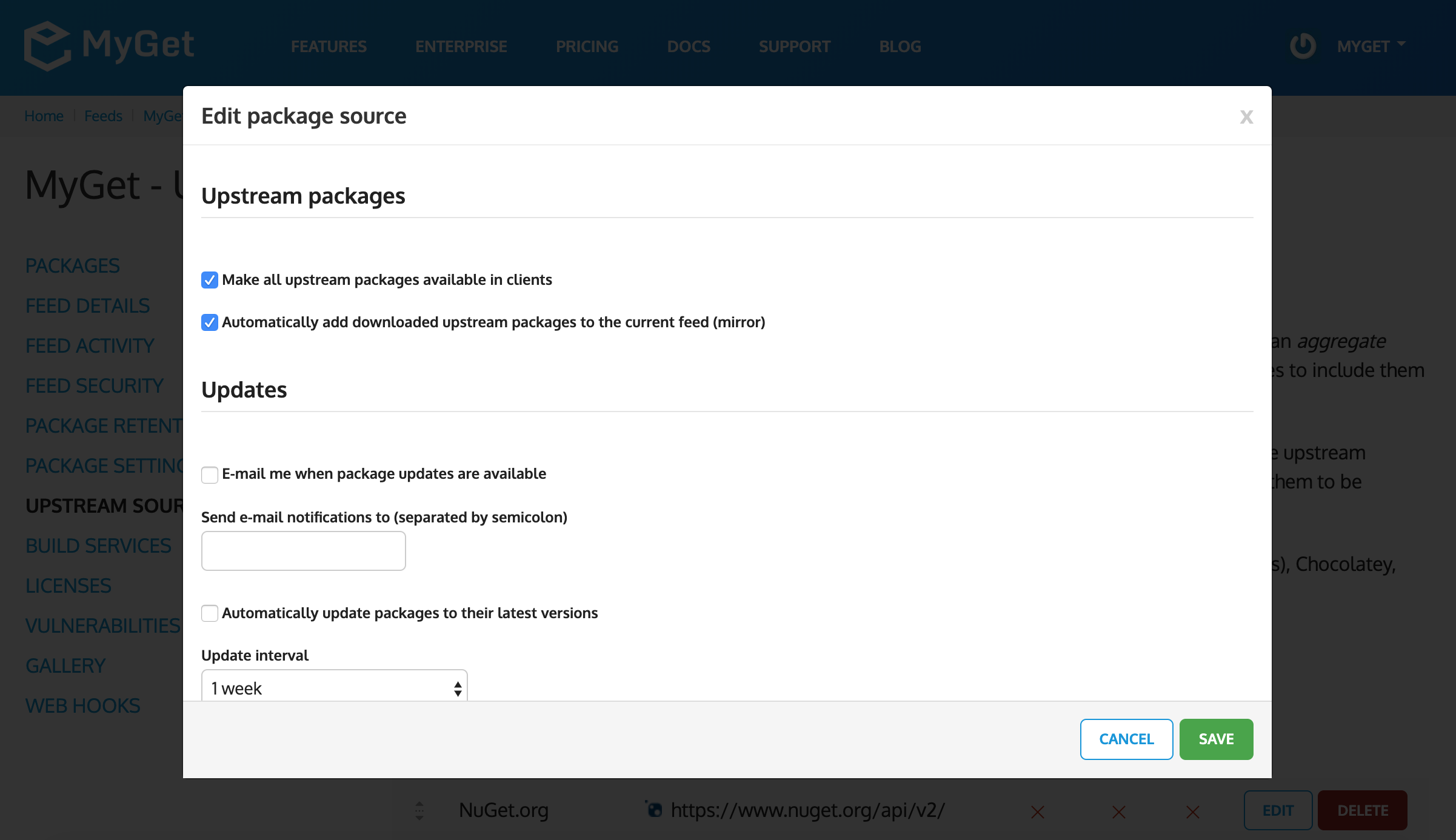
(optional) Enable upstream source proxy to seamlessly blend your MyGet feed with the pypi.org repository.
From the Upstream Sources tab, edit the Python upstream source and enable the Make all upstream packages available in clients option. If you prefer to have the package binaries downloaded to your feed for subsequent requests, also enable the Automatically add downloaded upstream packages to the current feed (mirror) option.
Working with your Python repository
In order to be able to fetch and install packages with pip tool you need to specify url under which your repository (feed) can be found.
a) for non private feed
pip install --index-url https://<your_myget_domain>/F/<your-feed-name>/python <package_name>
b) for private feed
pip install --index-url https://<username>:<password>@<your_myget_domain>/F/<your-feed-name>/python <package_name>
For your convenience, we recommend you to add these parameters to your pip.conf file in order to avoid unnecessary typing. Then your command for package installation will look like this:
pip install <package_name>
Please take a note, that if you try to install package that is not present on your MyGet feed, tool will fetch that package from main repository ( https://pypi.org/simple/ ).
If you have configured your pip tool and added some package to your feed, you are now able to install it.
There is often a situation when your package added to feed has some other dependencies. In that case if your package and its dependent packages are available on feed, pip will fetch and install these from that feed.
On the other hand, if dependencies are not available on your feed, pip will look for it on its main repository and install it along with your package which is placed on feed.
Keep in mind that if you want pip to install your package from feed, it must be mirrored on that feed
Installing specific version
For installing specific version you can use the same commands which pip normally exposes. For example in order to install version 0.0.4 of package A:
pip install --index-url https://<your_myget_domain>/F/<your-feed-name>/python A==0.0.4
If you don’t specify package version, the newest version of that package which is placed and mirrored on that feed will be installed.
Pushing a .whl package to your feed
You can easily upload a .whl package through the MyGet website, but if you prefer to automate this in a non-interactive way, you can still do so. You just need some tool like cUrl in order to push a .whl package from your command line:
curl -k -X POST https://<your_myget_domain>/F/<your_feed_name>/python/upload -H "Authorization: Bearer <your_access_token>" -F "data=@packageFileName.whl"
Be sure that packageFileName meets the requirements of the PEP 427 standard. (Please look at section File format of the standard document for more guidance.)
Read our contribution guidance or edit this page's source on GitHub.